Introduction #
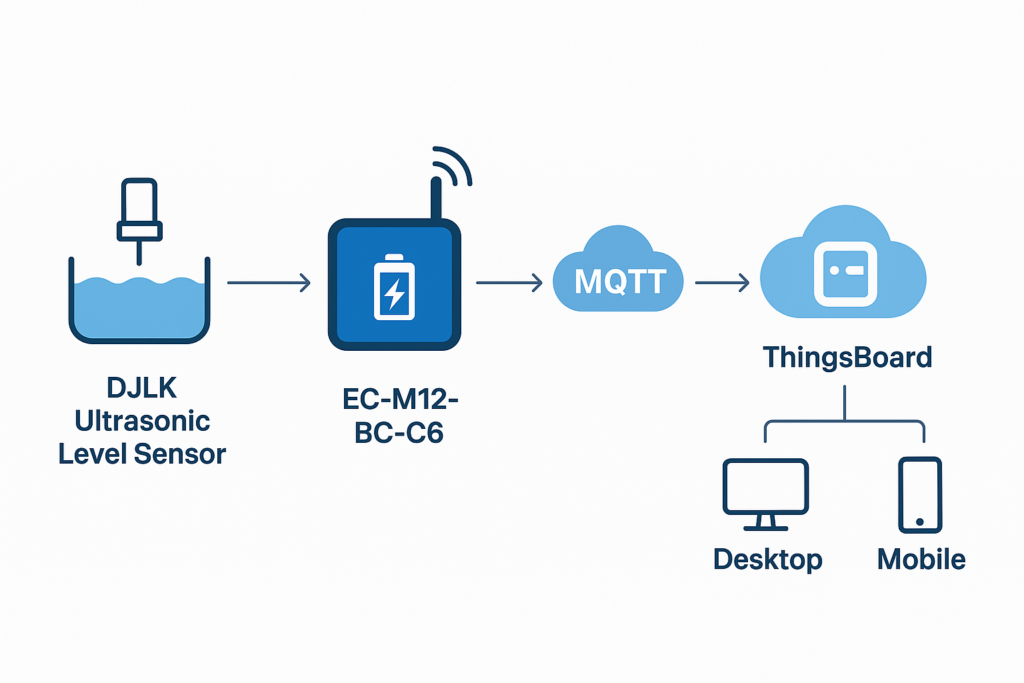
The EC-M12-BC-C6-C is a battery-powered data logger specifically designed for low-power remote monitoring applications. It integrates NB-IoT / LTE-M connectivity with Modbus RTU communication, enabling reliable and efficient data collection and transmission in industrial and IoT environments.
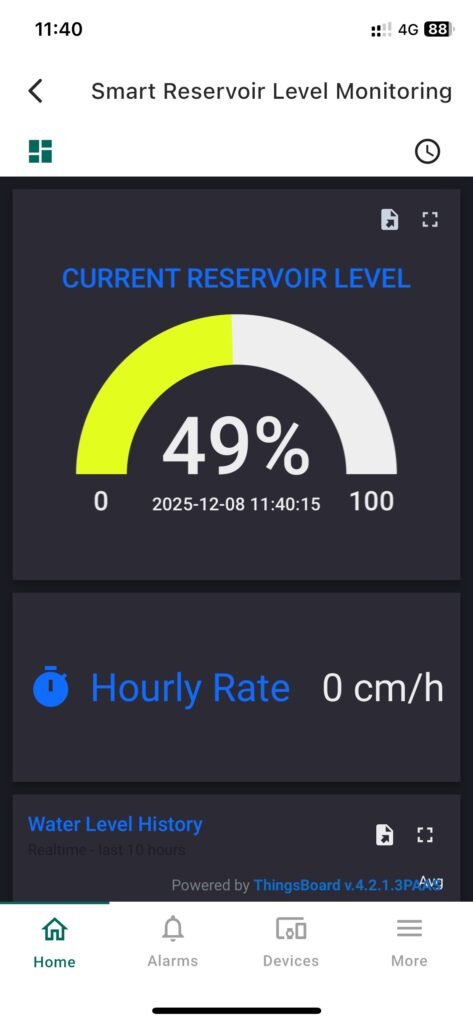
In this application, a DJLK ultrasonic level sensor is installed in a reservoir to continuously monitor water levels, hourly filling rates, and trigger alerts when predefined thresholds are reached. The system is fully integrated with a ThingsBoard cloud dashboard, providing real-time visualization and notifications accessible on both desktop and mobile devices.
Its low-power design allows long-term operation on battery, making it ideal for remote sites without grid power. This solution supports smart water management, irrigation, flood monitoring, and other applications requiring continuous, reliable remote monitoring.
System Architecture #
Hardware setup #
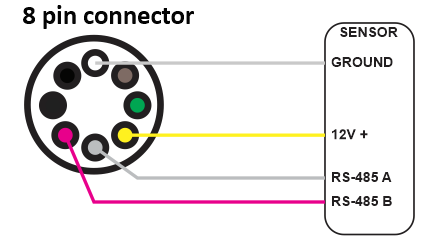
Connect DJLK Ultrasonic level sensor to 8 pin connector’s RS-485 line and powered the sensor using 12V output as figure 1.
Software setup #
- Define pin configurations as the datasheet.
- Initialize the modem
- Low power begin
- MQQT broker setup
- Enable the RS485 and booster
- Read DJLK Ultrasonic level sensor data via modbus and send it to the thingsboard dashboard
- Modbus registers from DJLK sensor
- 0x0100 → Processed level (cm)
- 0x0101 → Real-time level (cm)
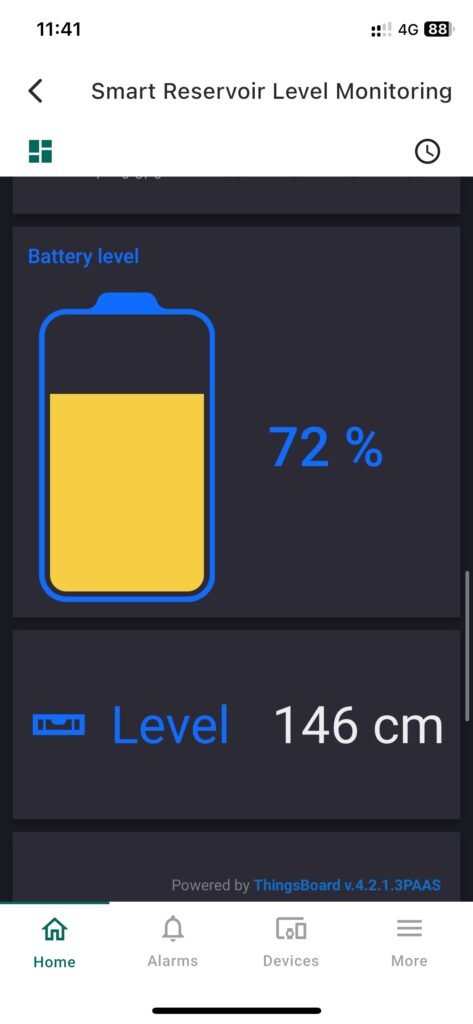
- Battery voltage measured via ADC, scaled to system voltage.
- Disable peripherals and booster and go to low power shutdown for 15 minutes.
Please refer below configured github link for full program: Smart Reservoir Level Monitoring System
ThingsBoard Dashboard Setup #
- Basic Setup: Follow the guide here for device token, topics, telemetry mapping, and basic widgets: Connecting ESP32 to ThingsBoard over Wi-Fi
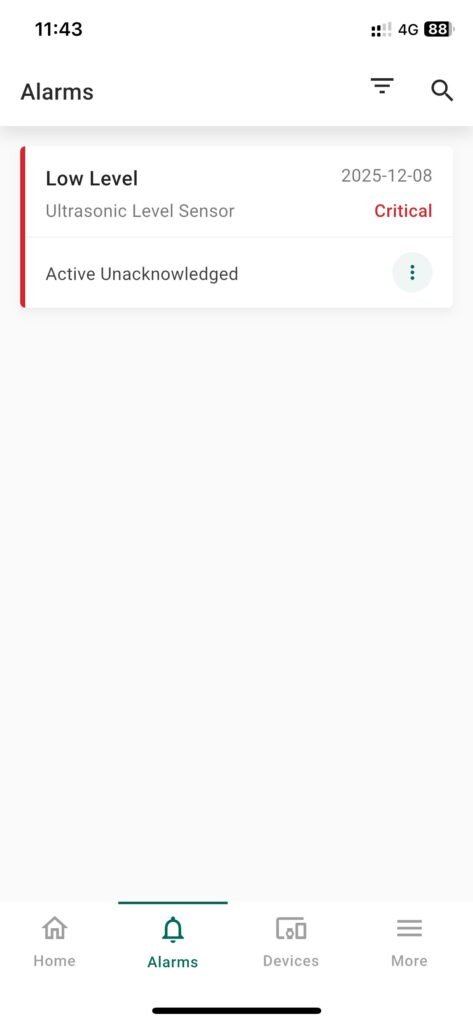
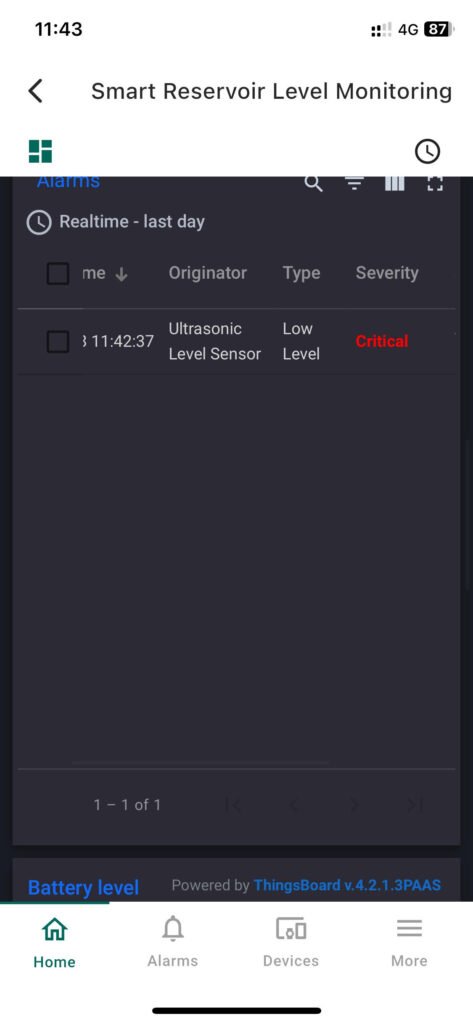
- Alarms Configuration:
- Go to Device Profile → Alarm Rules
- Define alarm types (e.g., High Level, Low Level)
- Set conditions using telemetry values (e.g., Processed_cm < threshold)
- Assign severity and notifications (email, SMS, dashboard popup)
- Save and apply the profile to your device
- Tips: New alarms will automatically trigger on the dashboard and can coexist with level indicators, trends, and notifications.
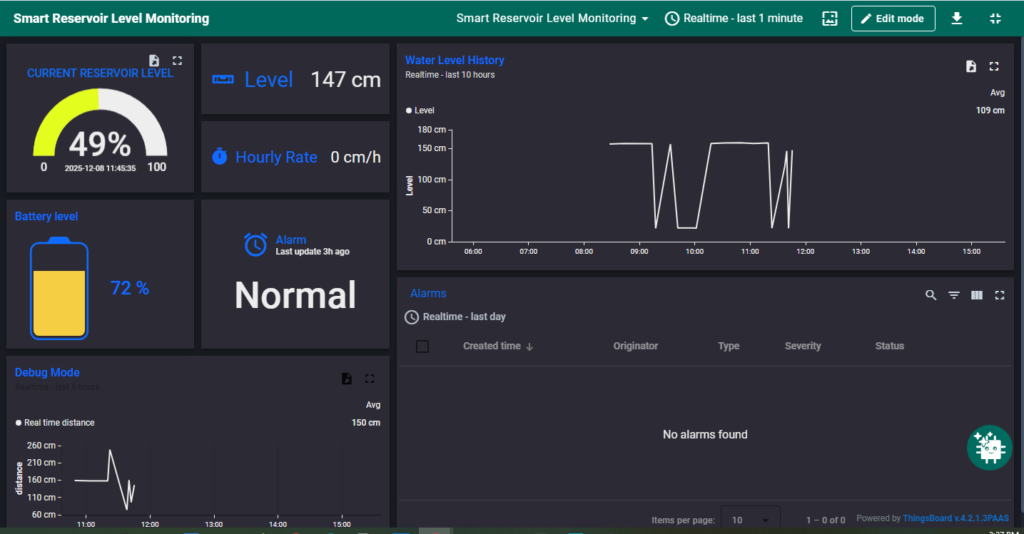
Smart Reservoir Level Monitoring Dashboard #
Desktop View #
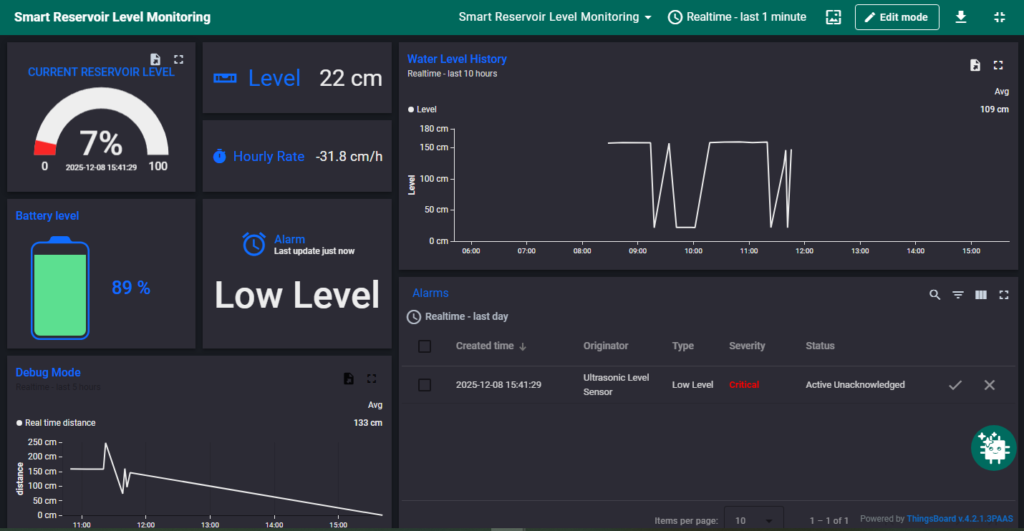
Mobile App View #
Power Consumption Analysis #
Power consumption of the system can divided into two main stages
- Modem initializing and data sending stage
- MCU sleep mode (Shutdown mode)
Modem initializing and data sending stage #
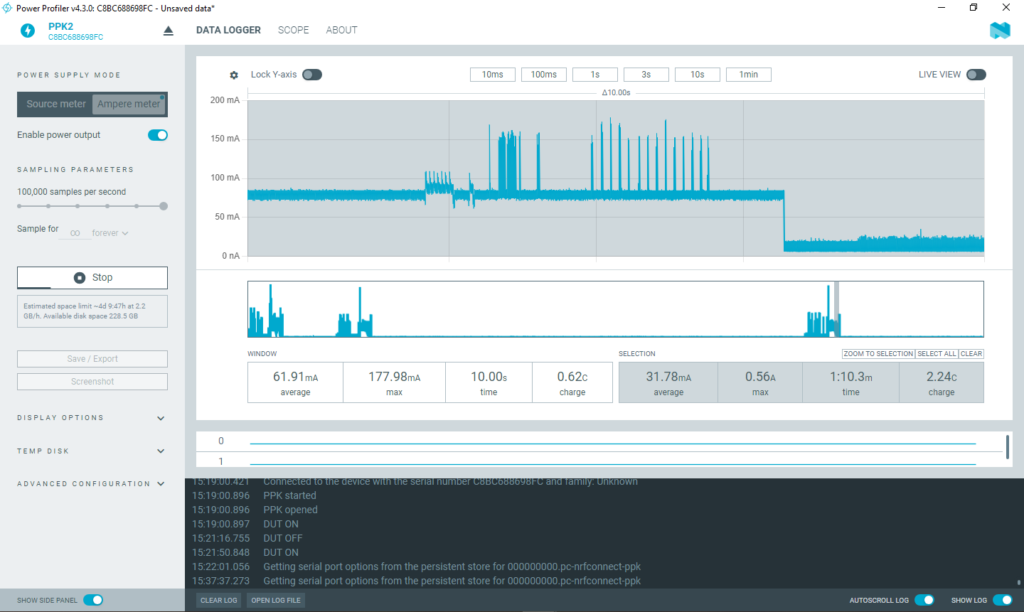
This period represents the active phase of the device, during which it performs all operational tasks such as initializing the modem, connecting to the network, reading the DJLK ultrasonic level sensor via the RS485 interface, and finally transmitting the data packet to the ThingsBoard cloud over MQTT.
On average, the device draws approximately 31.78 mA for about 70 seconds. During this time, the SIM7070 LTE modem establishes the network connection and generates several high-current spikes, reaching up to 0.56 A. Despite these peaks, the two lithium batteries connected in parallel are capable of supplying the required current without any issues.
A tantalum capacitor (1000 µF) placed close to the modem acts as a local energy reservoir, supplying the instantaneous surge current while the batteries maintain the average load.
According to the ER34615H (D) lithium primary battery datasheet, each cell can deliver a maximum pulse current of 300 mA for 100 milliseconds every 2 minutes. Based on power profile observations, the modem’s initialization phase produces current pulses exceeding 300 mA, lasting 30–40 milliseconds each. These pulses are within the battery’s safe operating capability, allowing the modem to initialize and operate reliably without excessive voltage drop or battery stress.
MCU sleep mode (Shutdown mode) #
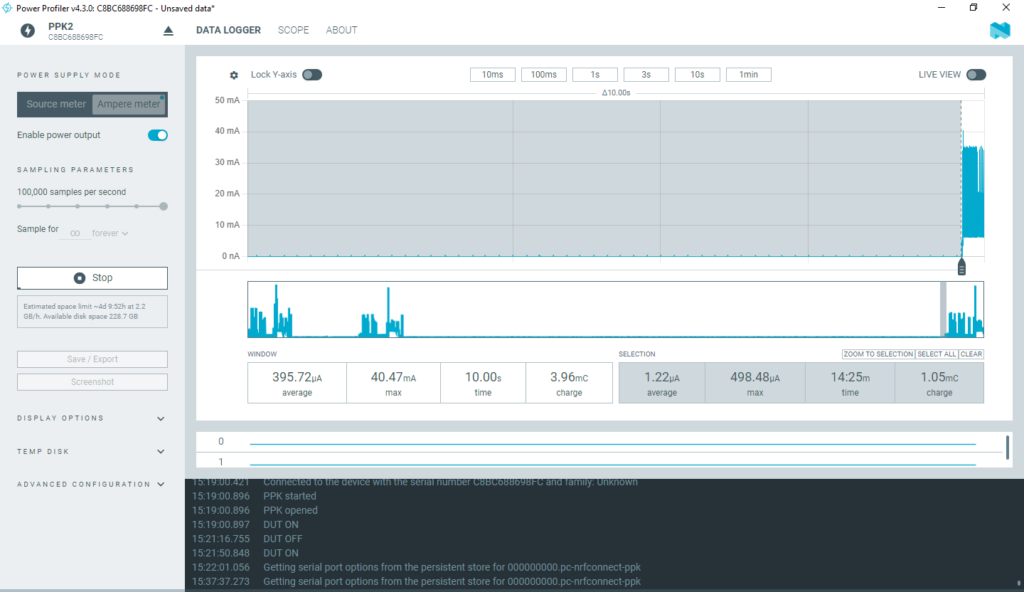
After data transmission is complete, the MCU enters shutdown mode, during which most peripherals and system clocks are powered down. Only the RTC (Real-Time Clock) remains active to keep track of time.
In this mode, the system draws a very low current of approximately 1.22 µA for a duration of 15 minutes.
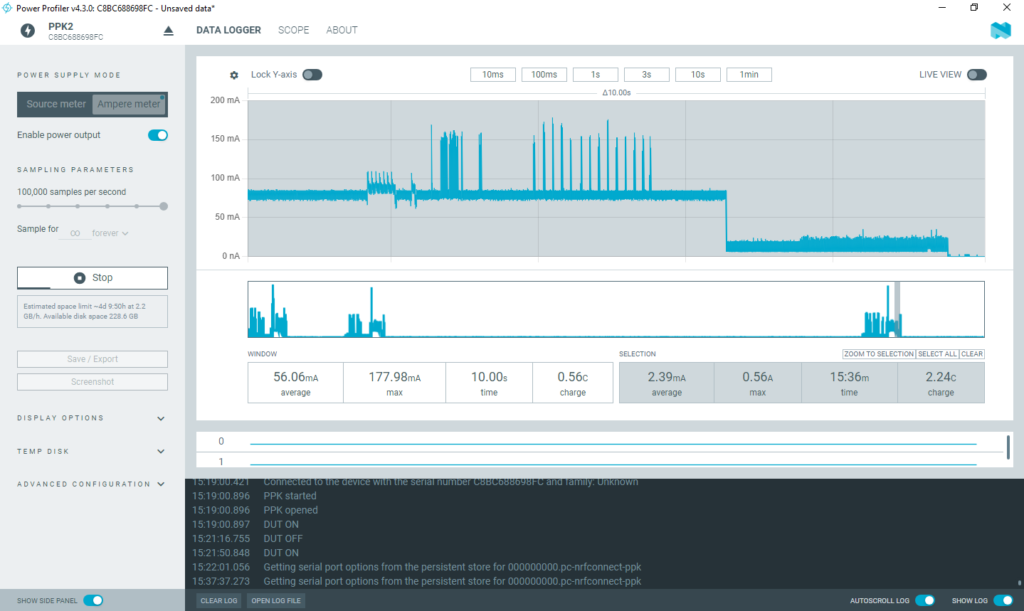
Below figure shows the whole system’s power profile which indicates the average current flow of 2.39mA. It has charge of 2.24c
| Stage | Mode | Average Current | Duration | Charge | Energy | Max current |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modem initialization and Data send | Shutdown | 31.78 mA | 70 seconds | 2.24C | 8.23 J | 560mA |
| Sleep (15 min) | Shutdown | 1.22µA | 15 min | 1.05mC | 0.0040 J | 498 µA |
| Send +sleep | Shutdown | 2.39mA | 16.10 min | 2.24C | 8.54 J | 560mA |
Battery Life Estimation #
EC-M12-BC-C6-C consists of two 19,000 mAh . So it has a total of 38,000 mAh battery power. As for the above collected data we have obtained battery life estimation when data is sent every 15 minutes and every 1 hour.
| Interval | Average Current per cycle | Estimated life (Hours) | Days | Months | Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Every 15 minutes | 2.39mA | 15899.6h | 662.5 days | 22.08 month | 1.815 years |
| Every 1 hour | 575 µA | 66086.9h | 2753.6 days | 91.78 month | 7.544 years |
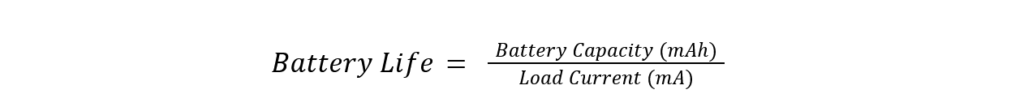
Below shows the formula to calculate average current and battery life for different intervals which help you to estimate the battery life for your application.
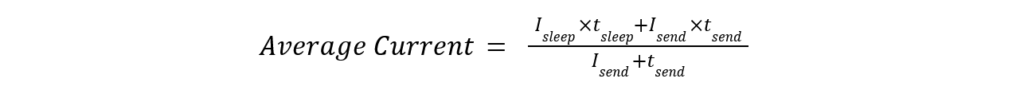
Optimization Tips #
To maximize battery life in remote deployments, the system can be optimized through several strategies:
- Increase the reporting interval: Sending data less frequently significantly reduces LTE-M transmission time, which is the highest power-consuming activity.
- Reduce sensor read frequency: The DJLK ultrasonic sensor should only be powered or read when necessary, avoiding unnecessary wake-ups.
- Extend sleep duration: Keeping the device in deep sleep for as long as possible ensures ultra-low current consumption during idle periods.
- The DJLK Ultrasonic level sensor consumes approximately 10 mA of current. Therefore, the overall battery life of your application will depend on the sensors used. Sensors with lower current consumption will increase battery life accordingly.
These adjustments allow the EC-M12-BC-C6-C to operate efficiently for long periods without needing battery replacement.
Opportunity for Low-Power Applications #
The low-power architecture of the EC-M12-BC-C6-C makes it suitable for deployments where long-term battery operation is essential. This includes environments where grid power is unavailable or difficult to access, such as:
- Remote reservoirs and irrigation tanks
- Agricultural fields and water distribution channels
- Flood monitoring points and riverbanks
- Rural and off-grid infrastructure
By combining efficient sleep cycles, optimized reporting intervals, and LTE-M connectivity, the device enables reliable, long-lasting monitoring in challenging low-power scenarios.
Application Scenarios / Use Cases #
Remote Reservoir Monitoring – Ideal for municipal water authorities, irrigation systems, and agricultural reservoirs. The device continuously tracks water levels, filling rates, and consumption patterns, ensuring reliable visibility of remote assets.
Flood or Drought Warning Systems – The system can detect sudden level changes and send early alerts to help prevent flooding or water shortages. Its long-range connectivity and low-power operation make it suitable for rivers, canals, and seasonal tanks.
Industrial or Smart City Deployments – Useful for monitoring water tanks, chemical storage systems, and automated liquid-level applications in factories, buildings, and urban infrastructure. Integration with ThingsBoard enables centralized monitoring and automated control.
Troubleshooting & FAQs #
- Connectivity Issues:
- Check GSM signal, SIM status, and MQTT broker connection.
- Battery or Power Issues:
- Verify battery voltage via ADC.
- Ensure peripherals and boosters are disabled during sleep.
- Sensor Read Errors:
- Confirm RS485 wiring, Modbus address, and DJLK sensor status.
- MQTT Payload Verification:
- Use MQTT client tools or ThingsBoard telemetry to confirm data delivery.
- Power Consumption Anomalies:
- Ensure low-power shutdown functions correctly.
- Check sleep interval and peripheral management.
Conclusion #
- Why EC-M12-BC-C6-C: Efficient, reliable, and easy to integrate, making it ideal for low-power remote monitoring.
- Low-Power Advantage: Long battery life, minimal maintenance, and unattended operation in remote areas.
- Future IoT Usability: Scalable to multiple reservoirs, supports additional sensors, and can integrate with smart IoT automation, enabling modern, data-driven water management.




