Programming #
The NORVI EC-M11-EG-C1-LTE has a mini USB port for serial connection with the SoC for programming. Any ESP32-supported programming IDE can be used to program the controller. Follow this guide to programming NORVI ESP32-based controllers with the Arduino IDE.
SoC: ESP32-WROOM32
Programming Port: USB UART
8-pin Connector and wire harness #
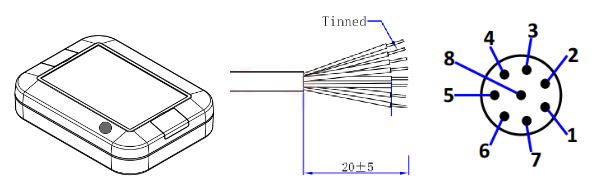
Pin Description #
| 8P Male | Wire color | I/O Configuration |
| 1 | White | Digital In 1 |
| 2 | Brown | Digital In 2 |
| 3 | Green | Analog In 1 |
| 4 | Yellow | Analog In 2 |
| 5 | Gray | Power+ |
| 6 | Pink | Power- |
| 7 | Blue | RS-485B |
| 8 | Red | RS-485A |
Digital Inputs #
Wiring Digital Inputs #
The digital inputs of NORVI EC-M11-EG-C1-LTE can be configured as both a sink and a source connection. The inverse of the digital input polar should be supplied to the common terminal.
Programming Digital Inputs #
Reading the relevant GPIO of the ESP32 gives the value of the digital input. When the inputs are in the OFF state, the GPIO goes HIGH, and when the inputs are in the ON state, the GPIO goes LOW. Refer to the GPIO allocation table in the datasheet for the digital input GPIO.
#define INPUT1 34
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Device Starting");
pinMode(INPUT1, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
Serial.print(digitalRead(INPUT1));
Serial.println("");
delay(500);
}0-10 V Analog Input #
Reading Analog Input #
Reading the relevant I2C address of the ADC gives the value of the analog input.
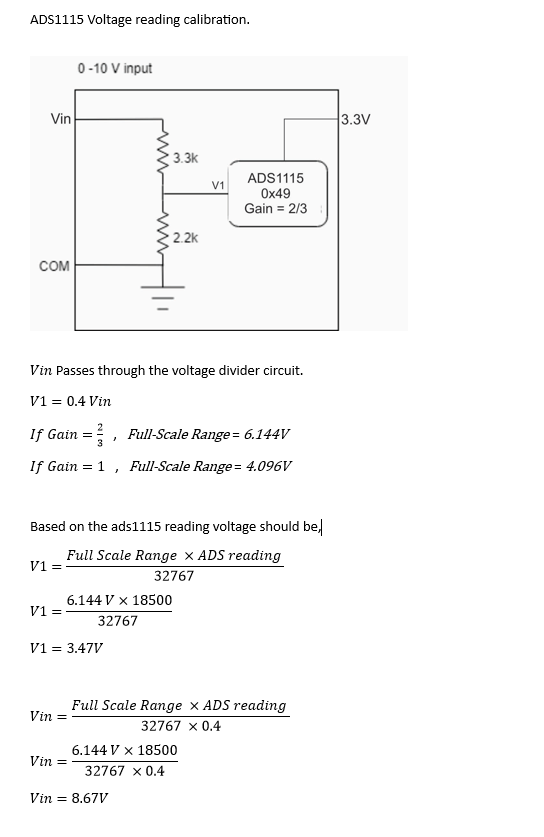
Programming Analog Inputs #
#include <Adafruit_ADS1X15.h>
#include <Wire.h>
Adafruit_ADS1115 ads1;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Device Starting");
Wire.begin(16,17);
ads1.begin(0x49);
ads1.setGain(GAIN_ONE);
}
void loop() {
Serial.print("Analog 0 ");
Serial.println(ads1.readADC_SingleEnded(0));
delay(10);
Serial.print("Analog 1 ");
Serial.println(ads1.readADC_SingleEnded(1));
delay(10);
Serial.print("Analog 2 ");
Serial.println(ads1.readADC_SingleEnded(2));
delay(10);
Serial.println("");
delay(500);
}RS-485 Communication #
| Driver | MAX485 |
| UART RX | GPIO4 |
| UART TX | GPIO2 |
| Flow Control | GPIO13 |
Programming RS-485 #
NORVI EC-M11-EG series RS-485 connection uses a half-duplex mode of MAX485 transmitter with UART
Communication.
#define RS485_FC 13
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Device Starting");
pinMode(RS485_FC, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(RS485_FC, HIGH); // Turns on Transmitter Mode
Serial.println("RS-485 Sending");
delay(500);
}LTE1 Communication #
| Model of LTE Modem | SIM7000-E |
| FCC ID | 2AJYU-SIM7000 |
| TAC | 86615402 |
| RXD | GPIO25 |
| TXD | GPIO26 |
| RESET | GPIO32 |
| POWER | GPIO22 |
LTE2 Communication #
| Model of LTE Modem | SIM7500 |
| FCC ID | 2AQ9M-SIM7500 |
| TAC | 86147503 |
| RXD | GPIO25 |
| TXD | GPIO26 |
| RESET | GPIO32 |
| POWER | GPIO22 |
Programming LTE Communication #
#define MODEM_RESET 32
#define MODEM_FLIGHT 22
#define MODEM_RX 26
#define MODEM_TX 25
long timer1;
void setup() { // initialize both serial ports:
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(MODEM_FLIGHT , OUTPUT); // FLIGHT MODE ENABLE
pinMode(MODEM_RESET , OUTPUT); // MODEM RESET PIN
digitalWrite(MODEM_FLIGHT, HIGH); // FLIGHT MODE
MODEM_RESET_CYC();
delay(2000);
Serial2.begin(115200, SERIAL_8N1, MODEM_RX, MODEM_TX);
Serial.println("SIM AT ATART >>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
delay(2000);
Serial2.println("AT");
delay(2000);
Serial2.println("AT+CPIN?");
delay(2000);
Serial2.println("AT+CNMP?");
}
void loop() {
delay(3000);
timer1 = millis();
Serial2.println("AT");
while(millis()<timer1+10000){
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
}
timer1 = millis();
Serial2.println("AT+CPIN?");
while(millis()<timer1+10000){
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
}
Serial.println("AT SCAN DONE"); // read from port 0, send to port 1:
while (Serial.available()) {
int inByte = Serial.read();
Serial2.write(inByte);
}
while (Serial2.available()) {
int inByte = Serial2.read();
Serial.write(inByte);
}
}
void MODEM_RESET_CYC() {
digitalWrite(MODEM_RESET,HIGH );
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(MODEM_RESET,LOW );
delay(1000);
digitalWrite(MODEM_RESET, HIGH);
}



